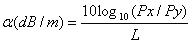Supercontinuum generation (SG) is a process where laser light is converted to light with a relatively broader spectral band width, whereas the spatial coherence usually remains high.
SG is usually accomplished by propagating optical pulses through a strongly nonlinear device, such as small core optical fibre. In some cases, tapered fibres can also be used.
[Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology; http://www.rp-photonics.com ]
Attenuation of an optical fibre is the loss of optical power as a result of absorption, scattering, bending, and other loss mechanisms as the light travels through the fibre.
The cutback method is often used for measuring the total attenuation of an optical fibre. The cutback method involves comparing the optical power transmitted through a longer piece of fibre to the power transmitted through a shorter piece of the fibre. The cutback method requires that a test fibre of known length ‘L’ be cut back to a shorter length. It needs access to both ends of the fibre. The cutback method begins by measuring the output power Py of the test fibre of known length ‘L’. Without disturbing the input conditions, the test fibre is cut back to a shorter length. The output power Px of the short test fiber is then measured and the fibre attenuation ‘A’ and the attenuation coefficient ‘a‘are calculated.
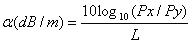
http://ioptic.blogspot.com/2011/08/cut-back-method-for-testing-fibre-loss.html
Researchers at Rochester Institute of Technology predict and observed an optical analogue of aerodynamic lift [Swartzlander, Nature photonics 2010].